What is Cisco CDP ? Benefits and Use Cases of CDP
In this article, we will learn about Cisco CDP feature, use cases, benefits and how to configure CDP feature on Cisco devices.
What is Cisco CDP? Benefits of using
Cisco CDP Concept
CDP stands for Cisco Discovery Protocol , a Cisco proprietary protocol that operates at layer 2 of the OSI model, allowing network devices to discover information about neighboring devices to build a fully connected tologogy.
CDP was developed in 1994 by Keith McCloghrie and Dino Farinacci, and is now used on all Cisco devices, such as Routers, Switches, Servers, Wifi…
Each Cisco device will periodically send CDP messages to the destination MAC address MAC L2 Multicast 01:00:0C:CC:CC:CC , out all connected ports. These packets can be received by Cisco devices, or other network devices that support the CDP protocol, from which other devices will get information about the device that is directly connected to them.
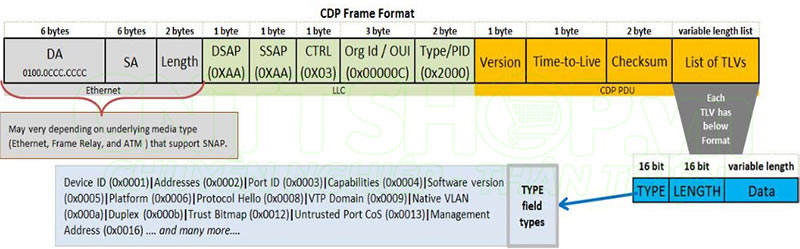
CDP currently has 2 versions CDPv1 and CDPv2. CDPv2 is the latest version currently and is used on all devices.
Benefits and limitations
CDP broadcast packets will include a lot of information related to the device such as firmware version, device hardware information, connected port, IP address... This information will vary depending on the type of device and firmware version of the device being used. Therefore, CDP has many benefits when you are troubleshooting network problems, checking the system... CDP will help administrators get an overview of the entire network system in operation.
CDP is a Cisco-specific protocol, so it will be limited to Cisco devices and some other manufacturers that use this protocol. If the model has many devices from many different manufacturers, you can use the LLDP protocol, which is equivalent in terms of usage. LLDP is an international standard protocol, so it will be supported on all different manufacturers.
CDP use cases and configuration
Use cases
With CDP, you can know how the devices are connected, and many other information related to that device. Therefore, CDP is very useful in many situations. For example, you have just been handed over the system, but have not been handed over information about the connection model, IP addresses of the switches. Or you are remotely configuring, and need to verify whether the connection information is correct according to the plan or not, then CDP is a very useful feature in these cases.
Configure CDP on Cisco devices
As for CDP configuration, you don't need to care, because CDP is enabled by default on all supported devices. You can enable or disable CDP with the command cdp run or no cdp run in global config mode, or cdp enable and no cdp enable in interface mode, if you only want to enable or disable on a specific number of ports.
| Core-Switch(config)# cdp run | Enable CDP on all devices |
| Core-Switch(config)# no cdp run | Disable CDP on all devices |
| Core-Switch(config)# interface g1 Core-Switch(config-if)# cdp enable |
Enable CDP on G1 port |
| Core-Switch(config)# interface g1 Core-Switch(config-if)# no cdp enable |
Disable CDP on G1 port |
In addition, there are also some options to change the information about the CDP timer, you can change it. However, in my opinion, it is not necessary, you should leave it as default. It is only related to how fast or slow CDP sends information update packets. By default, CDP will send packets every 60 seconds, and the hold time is 180 seconds.
| Core-Switch(config)# cdp holdtime [10-255] | Change the CDP hold time, value from 10 to 255 seconds. |
| Core-Switch(config)# cdp timer [5-254] | Change the time CDP sends packets, value from 5 to 254 seconds. |
You can also change the source interface, this is the IP on the switch that CDP will use to send CDP broadcast packets to, when you check CDP on the neighbor switch, you will see this IP information. Normally we will use the administrative IP range.
| Core-Switch(config)# cdp source-interface [interface-name] | Change the source interface that CDP uses to send packets. |
The device ID option will allow us to change the information displayed on the neighbor switch. You can set it as MAC address, serial number or hostname. The default will be MAC address.
| Core-Switch(config)# cdp device-id format [ mac/serial-number/hostname ] | Change the format of the device-id. |
CDP Test Commands
As for CDP configuration, it is very simple, you can leave everything as default. With CDP, what we need to care about most is the show commands to check.
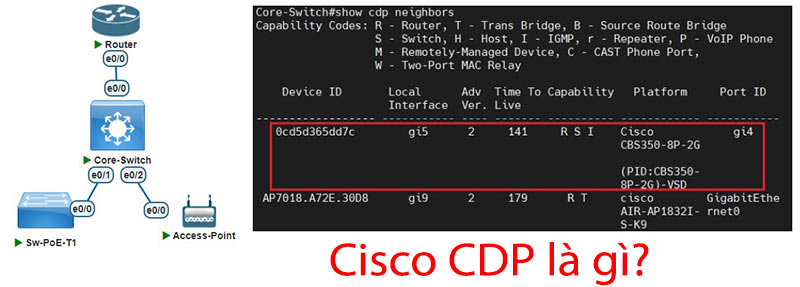
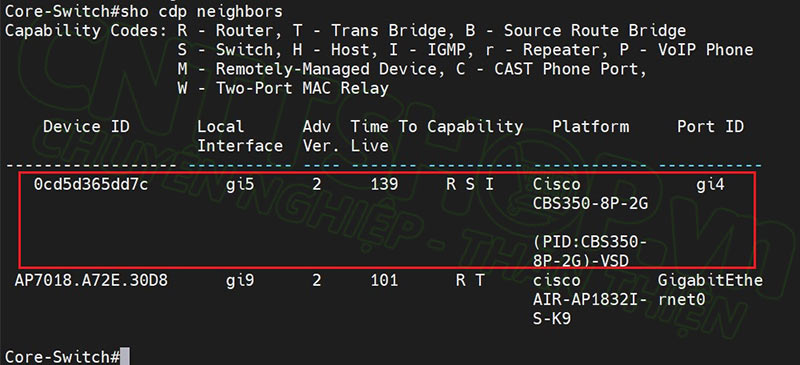
First is the show cdp neighbors command . This command will display all devices that are directly connected to the switch, and support the CDP protocol. If you use many devices that do not support CDP, you can use the LLDP protocol.
- The default Device ID will be the MAC address of the neighboring switch.
- Local Interface is the port on the switch you are accessing.
- Adv Ver is the advertisements version, currently all devices are version 2 by default.
- Time To Live is the remaining hold time, if the switch still receives advertisements packets, the neighbors information will still be kept on the switch. If the switch does not receive this packet, after 180 seconds, the switches will delete the neighbors information.
- Capability is the function of the device. For example, R here is Router, meaning that the neighboring device supports layer 3 features, related to routing. S is Switch, corresponding to Layer 2 features, and I is IGMP, you can see the information above.
- Platform is the type of device, you can know what device is connected.
- Port ID is the port on the neighboring device that is connected to this switch.
- In my example, I can know that port gi4 on CBS350-8P-2G is connecting to port gi5 on this Core switch.
To see detailed information about the connected device, you can add options behind. We can add the detail option , the switch will show detailed information of all the devices above. Normally, we should only show on each port. For example, I will check on port gi5, then you will add gi5 detail to the show cdp neighbors command .
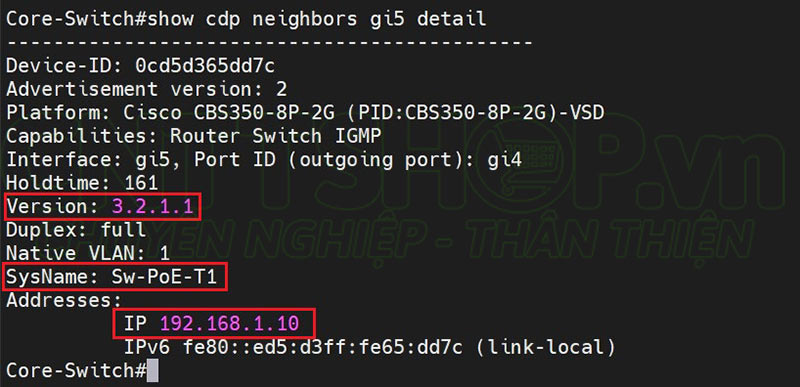
In addition to information about the connection port, you can learn more about the IP, this IP is the MGMT IP used as the source IP to send broadcast packets, hostname, firmware version...
Conclude
With each OS version or different device type, the information you show may be different. However, the main parameters such as connection port, device type, IP, version, hostname are similar. You can use CDP to check in case you need to find information about the connection model.
If you have any questions or suggestions, please leave a comment for everyone to discuss.
Good luck!





.png)

























.jpg)




























Bình luận bài viết!