Network Requirements
- Device1 is connected to PC1, Device2 is connected to PC2 and PC3, and the three PCs are in the same network segment. Device1 and Device2 are interconnected through Trunk ports.
- A dynamic aggregation group is configured between Device1 and Device2 for bandwidth increase, load sharing, and service backup.
Network Topology
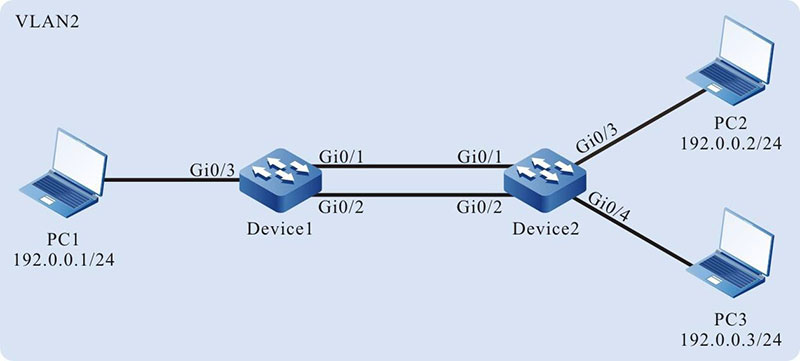
Figure 1-4 Networking for Configuring a Dynamic Aggregation Group
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Create a dynamic aggregation group.
#On Device1, create dynamic aggregation group 1.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config)#link-aggregation 1 mode lacp
|
#On Device2, create dynamic aggregation group 1.
|
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config)#link-aggregation 1 mode lacp
|
Step 2: Add ports into the aggregation group.
#On Device1, add ports gigabitethernet0/1 and gigabitethernet0/2 into aggregation group 1 in Active mode.
|
Device1(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/1,0/2
Device1(config-if-range)#link-aggregation 1 active
Device1(config-if-range)#exit
|
#On Device2, add ports gigabitethernet0/1 and gigabitethernet0/2 into aggregation group 1 in Active mode.
|
Device2(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/1,0/2
Device2(config-if-range)#link-aggregation 1 active
Device2(config-if-range)#exit
|
#After the configuration is completed, check the status of aggregation group 1 on the devices.
Here takes Device1 for example:
Device1#show link-aggregation group 1
Link Aggregation 1
Type: switchport
Mode: LACP
User: LAC
Description:
Peer-description:
Load balance profile: default
Number of ports in total: 2
Number of ports attached: 2
Root port: gigabitethernet0/1
gigabitethernet0/1: ATTACHED
gigabitethernet0/2: ATTACHED
According to the system display, ports gigabitethernet0/1 and gigabitethernet0/2 on Device1 are both in the ATTACHED state in aggregation group 1, and aggregation of aggregation group 1 is successful.

-
For the method of checking Device2, refer to the method of checking Device1.
Step 3: Configure the aggregation group to reference the load balance profile.
#On Device1, create the load balance profile linkagg-profile.
| Device1(config)#load-balance profile linkagg-profile |
#On Device1, configure the packet load hash-key in the load balance profile linkagg- profile, configure the L2 packet to load by the destination MAC, configure the IP packet to load by the destination IP.
|
Device1(config-hashprofile)#l2 dst-mac
Device1(config-hashprofile)#ip dst-ip
Device1(config-hashprofile)#active configuration pending
|
#On Device1, configure the load balance profile referenced by aggregation group 1 as linkagg-profile.
|
Device1(config)#interface link-aggregation 1
Device1(config-link-aggregation1)#load-balance profile linkagg-profile
|
# On Device2, create the load balance profile linkagg-profile (omitted).
#On Device2, configure the load hash-key of the packet in the load balance profile linkagg- profile, configure the L2 packet to load by the destination MAC, configure the IP packet to load by the destination IP. (Omitted)
#On Device2, configure the load balance profile referenced by aggregation group 1 as linkagg-profile. (Omitted)
Step 4: Configure a VLAN, and configure the link type of the aggregation group and ports.
#On Device1, create VLAN2, configure the link type of aggregation group 1 to Trunk and allow services of VLAN2 to pass, and set PVID to 2.
|
Device1(config)#vlan 2
Device1(config-vlan2)#exit
Device1(config)#interface link-aggregation 1
Device1(config-link-aggregation1)#switchport mode trunk
Device1(config-link-aggregation1)#switchport trunk allowed vlan add 2
Device1(config-link-aggregation1)#switchport trunk pvid vlan 2
Device1(config-link-aggregation1)#exit
|
#On Device1, configure the link type of port gigabitethernet0/3 to Access and allow services of VLAN2 to pass.
|
Device1(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/3
Device1(config-if-gigabitethernet0/3)#switchport mode access
Device1(config-if-gigabitethernet0/3)#switchport access vlan 2
Device1(config-if-gigabitethernet0/3)#exit
|
#On Device2, create VLAN2, configure the link type of aggregation group 1 to Trunk and allow services of VLAN2 to pass, and set PVID to 2.(Omitted)
#On Device2, configure the link type of ports gigabitethernet0/3 and gigabitethernet0/4 to Access and allow the services of VLAN2 to pass. (Omitted)
Step 5: Check the result.
#On the devices, check the aggregated bandwidth of aggregation group 1. Take Device1 for example:
Device1#show interface link-aggregation 1
link-aggregation 1 configuration information
Description :
Peer-description :
Status : Enabled
Link : Up
Act Speed : 2000
Act Duplex : Full
Port Type : Nni
Pvid : 2
According to the system display, the interface bandwidth of the aggregation group on Device1 is 2000 M.

-
For the method of checking Device2, refer to the method of checking Device1.
#After configuration, view the configured load balance profile on Device1.
Device1#show load-balance configuration
Profile:default
Configuration Valid currently:
L2: src-mac dst-mac
Ip: src-ip dst-ip
Configuration Valid-pending to be applied:
L2:
Ip:
Configuration Invalid-pending to be applied:
L2:
Ip: Profile:linkagg-profile
Configuration Valid currently:
L2: dst-mac
Ip: dst-ip
Configuration Valid-pending to be applied:
L2:
Ip:
Configuration Invalid-pending to be applied:
L2:
Ip:
#After the configuration is completed, check the current load balancing profile on Device1.
Device1#show link-aggregation group 1
Link Aggregation 1
Type: switchport
Mode: LACP
User: LAC
Description:
Peer-description :
Load balance profile: linkagg-profile
Number of ports in total: 2
Number of ports attached: 2
Root port: gigabitethernet0/1
gigabitethernet0/1: ATTACHED
gigabitethernet0/2: ATTACHED
According to the system display, the current load balancing profile referenced by aggregation group 1 is linkagg-profile.
#During the process of service interaction between PC1 and PC2 and PC3, load balancing of data is achieved on the aggregated links. If a link in the aggregation group becomes faulty, the other links provide service backup.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar![Module quang Inphi]() Module quang Inphi
Module quang Inphi![Module Quang Intel]() Module Quang Intel
Module Quang Intel![Module quang Finisar]() Module quang Finisar
Module quang Finisar![Module quang Ascent]() module-quang-ascent
module-quang-ascent Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng








.png)
























