Network Requirements
- Device2, Device3, Device4, and Device5 are in the same BGP AS 200. To reduce the number of IBGP full connections, they are divided into two different ASs in one BGP confederation.
- Set up EBGP neighbors between Device1 and Device2, and advertise route 100.0.0.0/24 to AS 200.
Network Topology
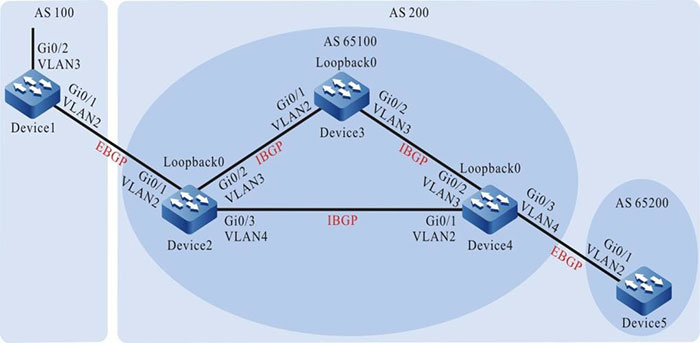
Figure 12–7 Networking for configuring a BGP confederation
|
Device
|
Interface
|
VLAN
|
IP Address
|
|
Device1
|
Gi0/1
|
2
|
1.0.0.1/24
|
|
Gi0/2
|
3
|
100.0.0.1/24
|
|
Device2
|
Gi0/1
|
2
|
1.0.0.2/24
|
|
Gi0/2
|
3
|
2.0.0.2/24
|
|
Gi0/3
|
4
|
3.0.0.2/24
|
|
Loopback0
|
|
20.0.0.1/32
|
|
Device3
|
Gi0/1
|
2
|
2.0.0.1/24
|
|
Gi0/2
|
3
|
4.0.0.1/24
|
|
Loopback0
|
|
30.0.0.1/32
|
|
Device4
|
Gi0/1
|
2
|
3.0.0.1/24
|
|
Gi0/2
|
3
|
4.0.0.2/24
|
|
Gi0/3
|
4
|
5.0.0.1/24
|
|
Loopback0
|
|
40.0.0.1/32
|
|
Device5
|
Gi0/1
|
2
|
5.0.0.2/24
|
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Configure the VLAN and join the interface to the corresponding VLAN. (Omitted)
Step 2: Configure the IP addresses of the interfaces. (Omitted)
Step 3: Configure OSPF so that loopback routes are reachable between devices.
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config)#router ospf 100
Device2(config-ospf)#network 2.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device2(config-ospf)#network 3.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device2(config-ospf)#network 20.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
Device2(config-ospf)#exit
|
#Configure Device3.
|
Device3#configure terminal
Device3(config)#router ospf 100
Device3(config-ospf)#network 2.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device3(config-ospf)#network 4.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device3(config-ospf)#network 30.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
Device3(config-ospf)#exit
|
#Configure Device4.
|
Device4#configure terminal
Device4(config)#router ospf 100
Device4(config-ospf)#network 3.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device4(config-ospf)#network 4.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device4(config-ospf)#network 5.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device4(config-ospf)#network 40.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
Device4(config-ospf)#exit
|
#Configure Device5.
|
Device5#configure terminal
Device5(config)#router ospf 100
Device5(config-ospf)#network 5.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device5(config-ospf)#exit
|
#Query the routing table of Device2.
Device2#show ip route ospf
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
U - Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external
O 4.0.0.0/24 [110/2] via 2.0.0.1, 00:02:42, vlan3
[110/2] via 3.0.0.1, 00:02:11, vlan4
O 30.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 2.0.0.1, 00:02:32, vlan3
O 40.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 3.0.0.1, 00:02:05, vlan4
#Query the routing table of Device3.
Device3#show ip route ospf
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B BGP, i-ISIS
U Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management, E - IRMP, EX IRMP external
O 3.0.0.0/24 [110/2] via 2.0.0.2, 00:03:24, vlan2
[110/2] via 4.0.0.2, 00:02:38, vlan3
O 20.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 2.0.0.2, 00:03:24, vlan2
O 40.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 4.0.0.2, 00:02:38, vlan3
#Query the routing table of Device4.
Device4#show ip route ospf
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B BGP, i-ISIS
U Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management, E - IRMP, EX IRMP external
O 2.0.0.0/24 [110/2] via 3.0.0.2, 00:03:42, vlan2
[110/2] via 4.0.0.1, 00:03:42, vlan3
O 20.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 3.0.0.2, 00:03:42, vlan2
O 30.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 4.0.0.1, 00:03:42, vlan3
#Query the routing table of Device5.
Device5#show ip route ospf
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B BGP, i-ISIS
U Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management, E - IRMP, EX IRMP external
O 2.0.0.0/24 [110/3] via 5.0.0.1, 00:00:03, vlan2
O 3.0.0.0/24 [110/2] via 5.0.0.1, 00:00:03, vlan2
O 4.0.0.0/24 [110/2] via 5.0.0.1, 00:00:03, vlan2
O 20.0.0.1/32 [110/3] via 5.0.0.1, 00:00:03, vlan2
O 30.0.0.1/32 [110/3] via 5.0.0.1, 00:00:03, vlan2
O 40.0.0.1/32 [110/2] via 5.0.0.1, 00:00:03, vlan2
According to the routing table, Device2, Device3, and Device4 have learnt the routes of the loopback interfaces of each other.
Step 4: Configure BGP connections in a confederation.
Configure IBGP connections in a confederation.
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2(config)#router bgp 65100
Device2(config-bgp)#neighbor 30.0.0.1 remote-as 65100
Device2(config-bgp)#neighbor 30.0.0.1 update-source loopback0
Device2(config-bgp)#neighbor 40.0.0.1 remote-as 65100
Device2(config-bgp)#neighbor 40.0.0.1 update-source loopback0
Device2(config-bgp)#neighbor 30.0.0.1 next-hop-self
Device2(config-bgp)#neighbor 40.0.0.1 next-hop-self
Device2(config-bgp)#exit
|
#Configure Device3.
|
Device3(config)#router bgp 65100
Device3(config-bgp)#neighbor 20.0.0.1 remote-as 65100
Device3(config-bgp)#neighbor 20.0.0.1 update-source loopback0
Device3(config-bgp)#neighbor 40.0.0.1 remote-as 65100
Device3(config-bgp)#neighbor 40.0.0.1 update-source loopback0
Device3(config-bgp)#exit
|
#Configure Device4.
|
Device4(config)#router bgp 65100
Device4(config-bgp)#neighbor 20.0.0.1 remote-as 65100
Device4(config-bgp)#neighbor 20.0.0.1 update-source loopback0
Device4(config-bgp)#neighbor 30.0.0.1 remote-as 65100
Device4(config-bgp)#neighbor 30.0.0.1 update-source loopback0
Device4(config-bgp)#exit
|
Configure EBGP connections in a confederation.
#Configure Device4.
|
Device4(config)#router bgp 65100
Device4(config-bgp)#neighbor 5.0.0.2 remote-as 65200
Device4(config-bgp)#exit
|
#Configure Device5.
|
Device5(config)#router bgp 65200
Device5(config-bgp)#neighbor 5.0.0.1 remote-as 65100
Device5(config-bgp)#exit
|
#On Device4, check the BGP neighbor status.
Device4#show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 40.0.0.1, local AS number 65100 BGP table version is 2
1 BGP AS-PATH entries 0 BGP community entries
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
5.0.0.2 4 65200 15 15 2 0 0 00:09:40 0
20.0.0.1 4 65100 9 9 2 0 0 00:07:49 0
30.0.0.1 4 65100 7 7 2 0 0 00:05:39 0
IBGP neighbors have been set up between Device4 and Device2 and between Device4 and Device3, and EBGP neighbors have been set up between Device4 and Device5.
Step 5: Configure a BGP confederation.
#Configure Device1.
Configure an EBGP peer. The AS number of the peer is confederation as ID 200.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config)#router bgp 100
Device1(config-bgp)#neighbor 1.0.0.2 remote-as 200
Device1(config-bgp)#network 100.0.0.0 255.255.255.0
Device1(config-bgp)#exit
|
#Configure Device2.
Configure the BGP confederation ID to 200, and configure an EBGP peer. The peer AS number is 100.
|
Device2(config)#router bgp 65100
Device2(config-bgp)#bgp confederation identifier 200
Device2(config-bgp)#neighbor 1.0.0.1 remote-as 100
Device2(config-bgp)#exit
|
#Configure Device3.
Configure the BGP confederation ID to 200.
|
Device3(config)#router bgp 65100
Device3(config-bgp)#bgp confederation identifier 200
Device3(config-bgp)#exit
|
#Configure Device4.
Configure the BGP confederation ID to 200, and configure the confederation to contain area 65100.
|
Device4#configure terminal
Device4(config)#router bgp 65100
Device4(config-bgp)#bgp confederation identifier 200
Device4(config-bgp)#bgp confederation peers 65200
Device4(config-bgp)#exit
|
#Configure Device5.
Configure the BGP confederation ID to 200, and configure the confederation to contain area 65200.
|
Device5(config)#router bgp 65200
Device5(config-bgp)#bgp confederation identifier 200
Device5(config-bgp)#bgp confederation peers 65100
Device5(config-bgp)#exit
|
Step 6: Check the result.
#On Device1, check the BGP neighbor status.
Device1#show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 100.0.0.1, local AS number 100 BGP table version is 2
1 BGP AS-PATH entries 0 BGP community entries
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
1.0.0.2 4 200 6 6 2 0 0 00:02:20 0
EBGP neighbors have been successfully set up between Device1 and Device2.
#On Device5, query the route information.
Device5#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 49, local router ID is 5.0.0.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
[B]*> 100.0.0.0/24 20.0.0.1 0 100 0 (65100) 100 i
Device5#show ip route bgp
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
U - Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external
B 100.0.0.0/24 [200/0] via 20.0.0.1, 00:00:38, vlan2
Device5 has successfully learnt route 100.0.0.0/24, and the next-hop property of the route keeps unchanged while the route is transmitted in the confederation. Device2, Device3, Device4, and Device5 belong to the same confederation, and full connections are not required. Device5 obtains external route information through Device4.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng




.png)
























