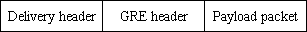Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a generic tunnel encapsulation protocol which defined how to use a network protocol to encapsulate another network protocol.
GRE tunnel is one tunnel technology among a lot of tunnel technologies. The starting point and end point of a tunnel need to be manually configured. The tunnel is a virtual end-to-end connection. It provides a transmission channel for the encapsulated packets. The two ends of the tunnel encapsulates and de-capsulates data packets respectively.
If a data packet needs to be transmitted through a GRE tunnel, the tunnel adds a GRE header to the packet header, and adds an IP header to the GRE header. Set the protocol number of the IP header to 47 (GRE protocol number in the IP header), set the source address of the IP header to the source address of the tunnel, and set the destination address of the IP header to the destination address of the tunnel.
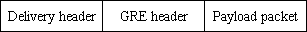
Payload packet: The network layer packet (such as IP packet) before it enters the tunnel is taken as the valid payload of the tunnel packet. The protocol of the packet is called the passenger protocol of the GRE tunnel.
GRE header: It refers to the GRE header that is added to the payload packet after the payload packet enters the tunnel. The GRE header contains the GRE protocol and some information related to the passenger protocol.
Delivery header: The encapsulated external protocol header (such as IP header) is the header of the protocol for the network in which the tunnel is located. It is a transmission tool which helps one protocol packet to traverse the network of another protocol.
After a packet is encapsulated at the starting point of a GRE tunnel, it selects a route according to the destination after encapsulation, and then it is sent out through the corresponding network interface. Intermediate devices take the packet as a common packet until the packet reaches the end of the tunnel.
Decapsulation is the reverse process of encapsulation. After the end point of the tunnel receives the packet, it analyzes Delivery header. If the end point of the tunnel finds that the destination is its own address, it checks the protocol field of the IP header. If the protocol field is 47 (GRE protocol number), the end point of the tunnel hands over the packet to the GRE tunnel for processing. The tunnel first removes Delivery header and then checks the protocol number, checksum, and keyword in the GRE header. After required processing, the tunnel removes the GRE header, and hands over the Payload packet to the passenger protocol for later processing. Then, the decapsulation is completed.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng




.png)