Configure IPv6-based VRRP Single-backup Group
Network Requirements
- On Device1 and Device2, create one single IPv6-based VRRP backup group so that Device1 and Device2 share the same virtual IPv6 link-local address and global address, realizing the backup for the default gateway of the user host and reducing the interruption time of the network.
Network Topology
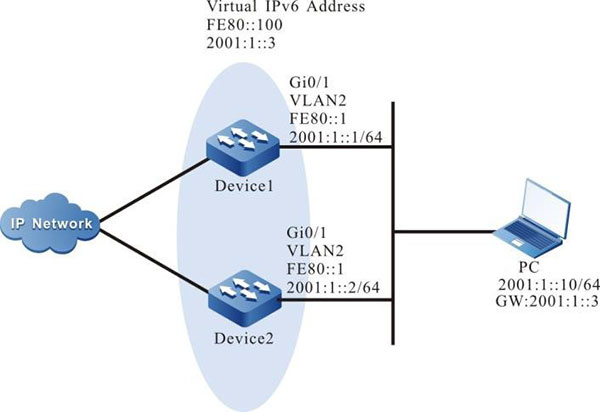
Figure 6-3 Networking of configuring IPv6-based VRRP single backup group
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Configure VLAN, and add the port to the corresponding VLAN (omitted).
Step 2: Configure the IPv6 address of the interface. Enable the switch of the RA response and RA periodical sending.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 address 2001:1::1/64
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#no ipv6 nd suppress-ra period
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#no ipv6 nd suppress-ra response
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#exit
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 address 2001:1::2/64
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#no ipv6 nd suppress-ra period
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#no ipv6 nd suppress-ra response
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#exit
|
Step 3: Create the IPv6-based VRRP group.
#On Device1, configure VRRPv3 group 1, the virtual IP address is 2001:1::3 and fe80::100, and configure the priority as 110.
|
Device1(config)#interface vlan2
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 vrrp 1 ip fe80::100 link-local
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 vrrp 1 ip 2001:1::3
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 vrrp 1 priority 110
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#exit
|
#On Device2, configure VRRPv3 group1 and the virtual IP address is 2001:1::3 and fe80::100.
|
Device2(config)#interface vlan2
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 vrrp 1 ip fe80::100 link-local
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 vrrp 1 ip 2001:1::3
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#exit
|
Step 4: Check the result.
#View the IPv6 VRRP status of Device1.
Device1#show ipv6 vrrp
Interface vlan2 (Flags 0x9)
Pri-addr : fe80::1
Vrf : 0
Pri-matchaddr : fe80::1
Virtual router : 1
Mac mode: real mac mode
Virtual IP address : fe80::100
Global address count:1
Global Match address : 2001:1::1
Global Virtual IP address : 2001:1::3
Virtual MAC address : 00-00-5e-00-02-01
State : Master
Normal priority : 110
Currnet priority : 110
Priority reduced : 0
Preempt-mode : YES
Advertise-interval : 100
Authentication Mode : None
#View the IPv6 VRRP status of Device2.
Device2#show ipv6 vrrp
Interface vlan2 (Flags 0x9)
Pri-addr : fe80::2
Vrf : 0
Pri-matchaddr : fe80::2
Virtual router : 1
Mac mode: real mac mode
Virtual IP address : fe80::100
Global address count:1
Global Match address : 2001:1::2
Global Virtual IP address : 2001:1::3
Virtual MAC address : 00-00-5e-00-02-01
State : Backup
Master addr : fe80::1
Normal priority : 100
Currnet priority : 100
Priority reduced : 0
Preempt-mode : YES
Advertise-interval : 100
Authentication Mode : None
We can see that the VRRPv3 status of Device1 is Master and the VRRPv3 status of Device2 is Backup. Device1 and Device2 share one virtual IP address. The host communicates with the network via the address. When Device1 fails, Device2 switches to Master at once for forwarding data.

-
The election principle of the VRRPv3 status is by priority. The one with large priority is Master. If the priorities are the same, compare according to the IP link-local address of the interface. The one with large IP address is Master.
- By default, VRRPv3 works in the preemption mode. The default priority is 100.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng




.png)
























