Network Requirements
- Run OSPF between Device1 and Device2, and run RIPv2 between Device2 and Device3.
- Device2 redistributes RIP routes to OSPF. To decrease the number of routes on Device1, summarize the redistributed RIP routes into summary route 20.0.0.0/16.
Network Topology
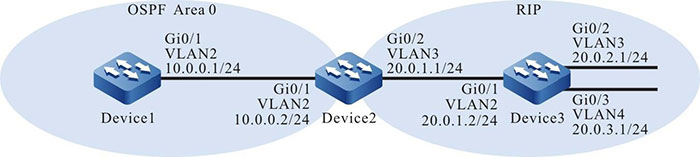
Figure 7-5 Networking for Configuring OSPF External Route Summary
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Create VLANs, and add ports to the required VLANs. (Omitted)
Step 2: Configure IP addresses for the ports. (Omitted)
Step 3: Configure OSPF and RIPv2.
#Configure OSPF for Device1.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config)#router ospf 100
Device1(config-ospf)#router-id 1.1.1.1
Device1(config-ospf)#network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device1(config-ospf)#exit
|
#Configure OSPF and RIPv2 for Device2.
|
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config)#router ospf 100
Device2(config-ospf)#router-id 2.2.2.2
Device2(config-ospf)#network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device2(config-ospf)#exit
Device2(config)#router rip
Device2(config-rip)#version 2
Device2(config-rip)#network 20.0.0.0
Device2(config-rip)#exit
|
#Configure RIPv2 for Device3.
Device3#configure terminal
Device3(config)#router rip
Device3(config-rip)#version 2
Device3(config-rip)#network 20.0.0.0
Device3(config-rip)#exit |
#Query the routing table of Device2.
Device2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:15:46, vlan2
C 20.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, 00:15:23, vlan3
R 20.0.2.0/24 [120/1] via 20.0.1.2, 00:12:17, vlan3
R 20.0.3.0/24 [120/1] via 20.0.1.2, 00:12:06, vlan3
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 03:34:27, lo0
Step 4: Configure OSPF to redistribute RIP routes.
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2(config)#router ospf 100
Device2(config-ospf)#redistribute rip
Device2(config-ospf)#exit
|
#Query OSPF LSDB of Device2.
Device2#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 100)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 1071 0x80000003 0x729f 1
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 873 0x80000004 0x38cd 1
Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum
10.0.0.2 2.2.2.2 1070 0x80000001 0x43d6
AS External Link States
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Route
20.0.1.0 2.2.2.2 365 0x80000001 0x7d04 E2 20.0.1.0/24 [0x0]
20.0.2.0 2.2.2.2 365 0x80000001 0x720e E2 20.0.2.0/24 [0x0]
20.0.3.0 2.2.2.2 365 0x80000001 0x6718 E2 20.0.3.0/24 [0x0]
According to the OSPF database, three external LSA have been generated, indicating that the RIP routes have been redistributed to OSPF.
#Query the routing table of Device1.
Device1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:56:40, vlan2
OE 20.0.1.0/24 [150/20] via 10.0.0.2, 00:02:40, vlan2
OE 20.0.2.0/24 [150/20] via 10.0.0.2, 00:02:40, vlan2
OE 20.0.3.0/24 [150/20] via 10.0.0.2, 00:02:40, vlan2
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 115:12:28, lo0
Device1 has learnt redistributed RIP routes.
Step 5: On the ASBR, configure OSPF external route summary. Now Device2 is the ASBR.
#Configure Device2 and summarize the redistributed RIP routes into 20.0.0.0/16.
|
Device2(config)#router ospf 100
Device2(config-ospf)#summary-address 20.0.0.0 255.255.0.0
Device2(config-ospf)#exit
|
Step 6: Check the result.
#Query OSPF LSDB of Device2.
Device2#show ip ospf database
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 100)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 1437 0x80000003 0x729f 1
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 1240 0x80000004 0x38cd 1
Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum
10.0.0.2 2.2.2.2 144 0x80000002 0x41d7
AS External Link States
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Route
20.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 84 0x80000001 0x88f9 E2 20.0.0.0/16 [0x0]
Comparing the result with the result in Step 3, you will find that the three external LSAs have been deleted, and a summarized external LSA has been generated.
#Query the routing table of Device2.
Device2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:28:03, vlan2
O 20.0.0.0/16 [110/1] is directly connected, 00:04:48, null0
C 20.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, 00:27:40, vlan3
R 20.0.2.0/24 [120/1] via 20.0.1.2, 00:24:34, vlan3
R 20.0.3.0/24 [120/1] via 20.0.1.2, 00:24:23, vlan3
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 03:46:44, lo0

-
In the routing table of Device2, a summary route 20.0.0.0/16 with the output interface being Null0 has been automatically added. This route helps to prevent routing loops.
#Query the routing table of Device1.
Device1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:58:40, vlan2
OE 20.0.0.0/16 [150/20] via 10.0.0.2, 00:15:26, vlan2
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 115:17:28, lo0
The routing table of Device1 has only learnt the summary route 20.0.0.0/16.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng




.png)
























