Network Requirements
- Device1, Device2, Device3, and Device4 runs the RIPng protocol and interconnects with each other.
- Device1 learns route 2001:5::/64 from both Device2 and Device3.
- On Device1, set the route metric offset in the receive direction so that Device1 selects the route advertised by Device2 with priority.
Network Topology
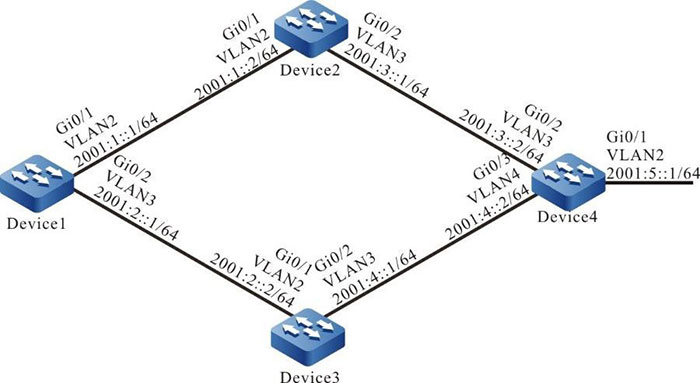
Figure 6-3 Networking for configuring the RIPng metric offset
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Create VLANs, and add ports to the required VLANs. (Omitted)
Step 2: Configure the IPv6 address of an interface (omitted).
Step 3: Configure RIPng.
#Configure Device1.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config)#ipv6 router rip 100
Device1(config-ripng)#exit
Device1(config)#interface vlan2
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device1(config-if-vlan2)#exit
Device1(config)#interface vlan3
Device1(config-if-vlan3)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device1(config-if-vlan3)#exit
|
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config)#ipv6 router rip 100
Device2(config-ripng)#exit
Device2(config)#interface vlan2
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device2(config-if-vlan2)#exit
Device2(config)#interface vlan3
Device2(config-if-vlan3)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device2(config-if-vlan3)#exit
|
#Configure Device3.
|
Device3#configure terminal
Device3(config)#ipv6 router rip 100
Device3(config-ripng)#exit
Device3(config)#interface vlan2
Device3(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device3(config-if-vlan2)#exit
Device3(config)#interface vlan3
Device3(config-if-vlan3)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device3(config-if-vlan3)#exit
|
#Configure Device4.
|
Device4#configure terminal
Device4(config)#ipv6 router rip 100
Device4(config-ripng)#exit
Device4(config)#interface vlan2
Device4(config-if-vlan2)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device4(config-if-vlan2)#exit
Device4(config)#interface vlan3
Device4(config-if-vlan3)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device4(config-if-vlan3)#exit
Device4(config)#interface vlan4
Device4(config-if-vlan4)#ipv6 rip enable 100
Device4(config-if-vlan4)#exit
|
#View the IPv6 route table of Device1.
Device1#show ipv6 route
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
U - Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
L ::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 2w5d:06:21:24, lo0
C 2001:1::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 00:02:05, vlan2
L 2001:1::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 00:02:04, lo0
C 2001:2::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 00:02:02, vlan3
L 2001:2::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 00:02:01, lo0
R 2001:3::/64 [120/2]
via fe80::201:7aff:fec3:38a4, 00:02:03, vlan2
R 2001:4::/64 [120/2]
via fe80::201:7aff:fe11:2214, 00:00:48, vlan3
R 2001:5::/64 [120/3]
via fe80::201:7aff:fec3:38a4, 00:02:03, vlan2
[120/3]
via fe80::201:7aff:fe11:2214, 00:00:48, vlan3
In the route table of Device1, you can see two routes to 2001:5::/64.
Step 4: Configure the access list.
|
Device1(config)#ipv6 access-list extended RIPng
Device1(config-v6-list)#permit 10 2001:5::/64 any
Device1(config-v6-list)#commit
Device1(config-v6-list)#exit
|
Step 5: Configure a metric offset.
#On Device1, configure the metric offset list and increase the metric of the route that has been learnt from interface vlan3 and matches ACL to 3.
|
Device1(config)# ipv6 router rip 100
Device1(config-ripng)#offset-list RIPng in 3 vlan3
Device1(config-ripng)#exit
|
Step 6: Check the result.
#View the IPv6 route table of Device1.
Device1#show ipv6 route
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
U - Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
L ::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 2w5d:06:34:28, lo0
C 2001:1::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 00:15:09, vlan2
L 2001:1::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 00:15:08, lo0
C 2001:2::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 00:15:06, vlan3
L 2001:2::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 00:15:05, lo0
R 2001:3::/64 [120/2]
via fe80::201:7aff:fec3:38a4, 00:03:10, vlan2
R 2001:4::/64 [120/2]
via fe80::201:7aff:fe11:2214, 00:03:10, vlan3
R 2001:5::/64 [120/3]
via fe80::201:7aff:fec3:38a4, 00:03:10, vlan2
According to the routing table of Device1, the next-hop output interface of route 2001:5::/64 is only vlan2, indicating that Device1 has selected the route advertised by Device2 with priority.

-
The route metric offset list can be applied to all interfaces or a specified interface, and it can be used in the receiving or advertising direction.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar![Module quang Inphi]() Module quang Inphi
Module quang Inphi![Module Quang Intel]() Module Quang Intel
Module Quang Intel![Module quang Finisar]() Module quang Finisar
Module quang Finisar![Module quang Ascent]() module-quang-ascent
module-quang-ascent Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng








.png)
























