SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is one standard protocol of managing Internet devices. It ensures that the management information can be transmitted between Network Management Station and managed device SNMP agent. It is convenient for the system administrator to manage the network system.
SNMP is one application layer protocol in the client/server mode. It mainly includes three parts:
- NMS (Network Management Station)
- SNMP agent
- MIB (Management Information Base).
The structure set of all managed objects maintained by the device is called MIB. The managed objects are organized according to the hierarchical tree structure. MIB defines the network management information got by one device. To be consistent with the standard network management protocol, each device should use the format defined in MIB to display the information. One subset of ISO ASN.1 defines the syntax for MIB. Each MIB uses the tree structure defined in ASN.1 to organize all available information. Each piece of information is one node with punctuation and each node contains one object ID and one short text description.
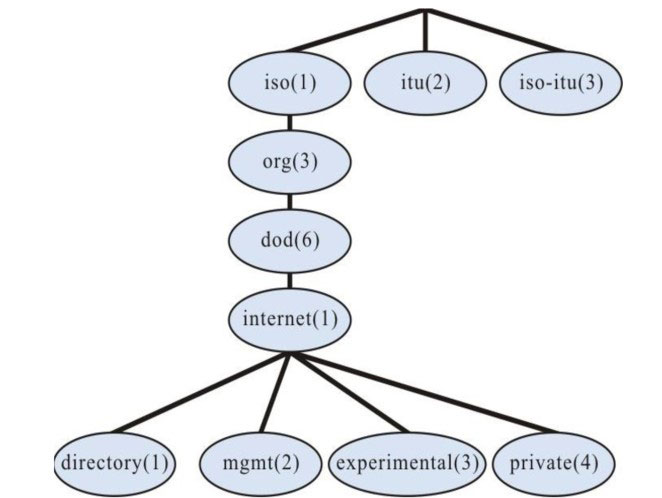
Figure 8–1 ASN.1 tree diagram of network management
SNMP protocol versions include SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3.
- SNMPv1: The first version of the SNMP protocol. The disadvantages: security problem, bandwidth waste, no communication capability between managers, the protocol only provides the limited operations;
- SNMPv2: It makes some improvement on the basis of SNMPv1, making the functions stronger and the security better;
- SNMPv3: original identity, information integrality and some aspects of re- transmission protect, content confidentiality, authorization and process control, the remote configuration and management capability needed by the above three capabilities;
Therefore, the development of SNMPv3 is centralized on two targets, that is, provide the workable security platform at the enhanced architecture and maintain the consistency of the network management system.
The SNMP protocol mainly includes the following operations:
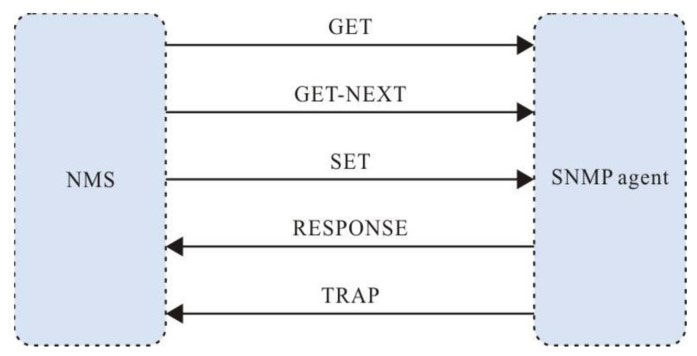
Figure 8–2 SNMP management operation diagram
- Get-request: SNMP network work station gets one or multiple parameters from the SNMP agent.
- Get-next-request: SNMP network work station gets the next parameter of one or multiple parameters from the SNMP agent.
- Get-bulk: SNMP network work station gets the batch parameters from the SNMP agent.
- Set-request: SNMP network work station sets one or multiple parameters of the SNMP agent.
- Get-response: SNMP agent returns one or multiple parameters and it is the responding operation of the SNMP agent for the above three operations.
- Trap: The packet sent by the SNMP agent actively, informing that something happens to the SNMP network work station.
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 use the authentication name to check whether to have the right to use the MIB object, so only when the authentication name of the network work station is consistent with one authentication name defined in the device, we can manage the device.
The authentication name has the following two attributes:
- Read-only: The read authority of the authorized network work station for all MIB objects of the device;
- Read-write: The read and write authority of the authorized network work station for all MIB objects of the device.
SNMPv3 determines which security mechanism to be adopted to process the data by the security model and the security level. There are three security models: SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3.
Table 8–1 Supported security model and security level
|
Security Model
|
Security Level
|
Authentication
|
Encryption
|
Description
|
|
SNMPv1
|
NoAuthNoPriv
|
Authentication name
|
None
|
Confirm the data validity via the authentication name.
|
|
SNMPv2c
|
NoAuthNoPriv
|
Authentication name
|
None
|
Confirm the data validity via the authentication name.
|
|
SNMPv3
|
NoAuthNoPriv
|
User name
|
None
|
Confirm the data validity via the user name.
|
|
SNMPv3
|
AuthNoPriv
|
MD5/SHA
|
None
|
Use HMAC-MD5/HMAC-SHA data authentication mode.
|
|
SNMPv3
|
AuthPriv
|
MD5/SHA
|
DES
|
Use the HMAC- MD5/HMAC-SHA data authentication mode and CBC-DES data encryption mode.
|
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar![Module quang Inphi]() Module quang Inphi
Module quang Inphi![Module Quang Intel]() Module Quang Intel
Module Quang Intel![Module quang Finisar]() Module quang Finisar
Module quang Finisar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng







.png)

























