When configuring the public attribute parameters and if the 802.1X authentication function, secure channel authentication, or MAC address authentication function is not enabled in the port, the configured function does not take effect.
When configuring the IP authorization function on the port, you need to configure the ARP keepalive function at the same time.
The controlled direction of the port includes bi-directional controlled and uni-directional controlled.
The function is used with the WOL (Wake On Lan) function. Some terminal is in the dormant state, but its network card still can process some special packets, such as WOL packets. After the network card receives the WOL packets, enable the terminal device and enter the working state.
When the access port of the dormant terminal enables the authentication function, you can configure the port as the uni-directional controlled, ensuring that the WOL packets can be forwarded to the terminal normally. After the terminal starts, it can initiate the authentication. After passing the authentication, it can access the network resources normally.
When sending the WOL packets across the segment, it is necessary to configure the ARP forwarding entry on the authentication device.
After enabling the authenticable host list function, only permit the user whose MAC address is in the authenticable host list to authenticate and the authentications initiated by the other users are refused.
When enabling the IP authorization function on the port and if finding that the IP address of the authentication user changes, force the user offline, including the following modes:
dhcp-server: When configuring the mode, it is necessary to configure the DHCP Snooping function on the device. After the authentication user gets the IP address from the DHCP server, record the binding relation of the authentication user and IP address on the device. If finding that the IP address of the user changes, force the user offline.
radius-server: RADIUS Server encapsulates the IP address used encapsulating the authentication user in the Frame-IP-Address field in the RADIUS packet and the authentication device records the binding relation of the user and the IP address. If finding that the user IP address changes, force the user offline.
Supplicant: After the user passes the first authentication, the device records the binding relation of the authentication user and IP address. If finding that the user IP address changes, force the user offline.
bind-mac-ip: MAC+IP binding mode, after the authentication user passes the first authentication, a MAC + IP binding entry will be generated and the entry configuration will be saved. Later, only the IP address in the binding entries generated when the first authentication is passed can be used to access the network.
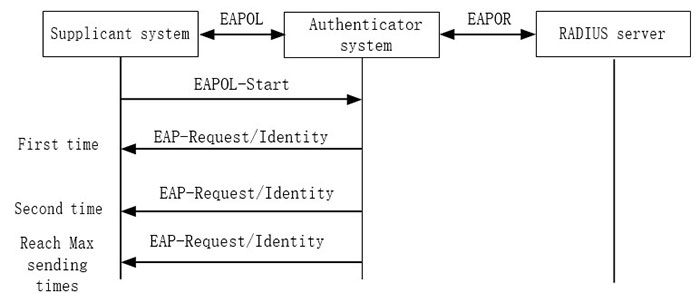
After the authentication device receives the EAPOL-Start packets sent by the client, send the authentication request EAP-Request/Identity packet to the client. If the authentication device does not receive the response packet, re-transmit the packet. The function is used to configure the maximum sending times of the EAP-Request/Identity packet. If the sending times exceeds the configured maximum value, the authentication device judges that the client is disconnected and ends the authentication.
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure the maximum sending times of the authentication request packets
|
dot1x max-reauth count
|
Mandatory
By default, the maximum sending times of the authentication request packet on the port is 3.
|
Configure Max. Sending Times of Authentication Packet
During the authentication, the authentication device sends the other EAP-Request packets except for EAP-Request/Identity packets to the client, such as EAP-Requesst/MD5 chanllenge packet. If the authentication device does not receive the response packet, re-transmit the packet. The function is used to configure the maximum sending times of the packet. If the sending times exceeds the configured maximum value, the authentication device judges that the client authentication fails.
The process of re-transmitting the EAP-Request packet is as follows:
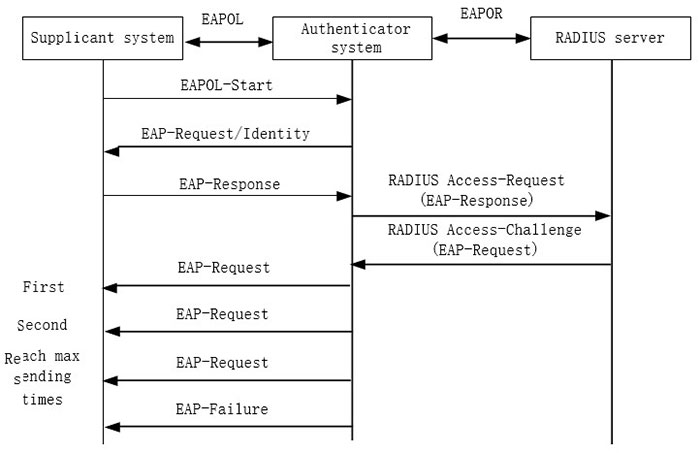
Figure 12-5 Re-transmit the EAP-Request packet
Table 12-23 Configure the maximum sending times of the authentication packet
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure the maximum sending times of the authentication packet
|
dot1x max-req count
|
Mandatory
By default, the maximum sending times of the authentication packet on the port is 2.
|
Configure Authentication Failure Record Log Function
After enabling the authentication failure record log function, the authentication device will record the information about the authentication failure, so as to detect the fault reason.
Table 12-24 Configure the authentication failure record log function
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure recording data log function
|
dot1x logging security-data {abnormal-logoff | failed-login | normal-logoff | successful-login }*
|
Mandatory
By default, the function of recording data log is not enabled on the port.
|
Configure ARP Keepalive Function
To check whether the user is online after the terminal user passes the authentication, the authentication device sends the ARP request packets to the authenticated user. The authentication device confirms whether the user is online by whether receiving the ARP response packet of the user.
Table 12-25 Configure the ARP keepalive function
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure the ARP keepalive function
|
dot1x client-probe { enable | disable }
|
Mandatory
By default, the ARP keepalive function under the port is disabled.
|

-
The authentication device can trigger ARP keepalive function normally only after getting the authenticated user IP address. If not receiving the ARP response packet of the authentication device during the protection period, force the user offline.
Configure Maximum Users of a Port
After the number of the authenticated users in the port reaches the configured threshold, the authentication system does not answer the new authentication request initiated by the user.
Table 12–26 Configure the maximum users of the port
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure the maximum users of the port
|
authentication max-user-num max-uer-num-value
|
Mandatory
By default, the maximum number of the users permitted to be connected in the port is 256.
|

-
The port needs to be configured as the user-based access control mode (Macbased). Otherwise, the configured access users cannot take effect.
Configure IP ACL Prefix Name
After the end user authentication is successful, when the server sends the IP ACL with the number greater than 2000, it is required to configure the IP ACL with the name as "IP ACL prefix name+ACL number" on the device. For example, the server sends the ACL with the number as 2001 and then configure the IP ACL with the name as "assignacl-2001" on the device.
Table 12-27 Configure the IP ACL prefix name
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter the global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Configure the IP ACL prefix name
|
dot1x number-acl-prefix number-acl-prefix-name
|
Mandatory
By default, the IP ACL prefix name is "assignacl-".
|

-
When the access control mode is configured as port-based multi-host mode (portbased host-mode multi-hosts), delivering the ACL function does not take effect.
Configure Default Valid VLAN
When the server does not send the VLAN (Auto VLAN), this configuration can be used to specify the VLAN if the authenticated users are expected to communicated in the specified VLAN.
Table 12-28 Configure the default valid VLAN
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter the global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Configure the default valid VLAN
|
dot1x default-active-vlan default-active-vlan-id
|
Mandatory
By default, the default valid VLAN is not configured.
|

-
The priority of the binding relationship after the user authentication is in the following order: server sending the VLAN, default valid VLAN, VLAN which the PVID of the interface locates in.
- When the port is configured based on the user access control mode (macbased), the default effective VLAN will take effect when the port meets the VLAN mode of hybrid mode and MAC VLAN condition is enabled.
Configure to Allow Unauthenticated User to Communicate in VLAN which PVID Locates in
When multiple interfaces access to the interface, each terminal needs to perform the access control. Some terminals that cannot initiate the 802.1X authentication also hopes to visit the network resources and you can enable the command. After the function is enabled, the unauthenticated end user can normally communicate in the VLAN which the PVID locates in.
This function must meet the following functions to ensure normal running.
- Enable the 802.1X authentication or MAC address authentication on the interface.
- The access control mode of the interface is the user-based access control mode (Macbased).
- Port VLAN mode is Hybrid mode.
- The function of only receiving the Untag packet needs to be enabled on the interface.
Table 12-29 Configure to allow the unauthenticated user to communicate in the VLAN which the PVID locates in
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter the global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Configure to allow the unauthenticated user to communicate in the VLAN which the PVID locates in
|
dot1x native-vlan-free
|
Mandatory
By default, the function of allowing the unauthenticated user to communicate in the VLAN which the PVID locates in is disabled,
|

-
After the function is enabled on the interface, the function of only receiving the untage packet needs to be enabled on the interface by configuring the switchport accept frame-type untag command on the interface to ensure that the packet sent by the unauthenticated user can only be forwarded in the VLAN which the PVID locates in.
- It is recommended that this function be used together with the VLAN sent by the server or the default valid VLAN.
- The function does not support the secure channel authentication.
Configure Port Access Control Mode
There are two kinds of port access control modes: port-based access control mode and user-based access control authentication mode.
Port-based access control mode (Portbased): In the port, only permit one user authentication to pass;
User-based access control mode (Macbased): In the port, permit multi-user authentication to pass. The users in the port need to pass the authentication respectively so that they can access the network.
Port-based access control mode includes two kinds: multi-host mode and single-host mode.
Multi-host mode (Multi-hosts): After one user in the port passes the authentication, the other users in the port can access the network without authentication.
Single-host mode (Single-host): In the port, only permit one user to pass the authentication and access the network; the other users cannot access the network and also cannot pass the authentication.
Table 12-30 Configure the port access control mode
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
|
Configure the access control mode
|
authentication port-method { macbased | portbased }
|
Mandatory
By default, enable the user authentication mode in the port.
|
|
Configure the port-based access control mode
|
authentication port-method portbased host-mode { multi-hosts | single-host }
|
Optional
By default, enable the multi-host authentication mode in the port.
|

-
When configuring the host mode of the port-based access control mode, we need to ensure that the access control mode is configured as the port-based access control mode (Portbased).
Configure Guest VLAN
The user can get the 802.1X client software in Guest VLAN to upgrade the client, or execute other application program (such as anti-virus software and operation system patch) upgrade.
Table 12-31 Configure Guest VLAN
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure Guest VLAN
|
authentication guest-vlan guest-vlan-id
|
Mandatory
By default, Guest VLAN is not configured in the port; the value range is 1-4094.
|

-
Guest VLAN of the port cannot be applied to the dynamic VLAN. If VLAN ID specified by Guest VLAN is the VLAN automatically created by GVRP, Guest VLAN can be configured successfully, but cannot take effect.
- To ensure that the functions can be used normally, please distribute different VLAN IDs for Voice VLAN, Private VLAN, and Guest VLAN.
Configure Guest ACL
If the user does not pass the authentication, we can configure Guest ACL in the port to limit the resources accessed by the user in Guest VLAN.
Table 12-32 Configure Guest ACL
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure Guest ACL
|
authentication guest-acl
guest-acl-name
|
Mandatory
By default, Guest ACL is not configured in the port.
|

-
If Guest VLAN is not configured in the port, the configured Guest ACL does not take effect.
- Guest ACL can take effect only in the user-based access control mode (Macbased).
- The ACL rule is configured in the authentication device.
Configure Critical VLAN
When the user adopts the RADIUS authentication, the authentication server is not available and as a result, the authentication fails. Permit the user to access the resources in the specified VLAN and the VLAN is called Critical VLAN.
When the port is configured as the port-based access control mode and there is user to authenticate on the port, but all authentication servers are not available, the port is added to Critical VLAN and all users under the port can access the resources in the Critical VLAN.
When the port is configured as user-based access control mode and there is user to authenticate on the port, but all authentication servers are not available, the user is only permitted to access the resources in Critical VLAN.
If the port is configured as the user-based access control mode, it should meet the following conditions to run normally:
- Port VLAN mode is Hybrid mode
- The port enables the MAC VLAN function. The user in the Critical VLAN initiates the authentication. If the authentication server is still not available, the user is still in Critical VLAN. If the authentication server is available, the user exits Critical VLAN with the authentication result.
After the port is added to Critical VLAN and if the authentication device is configured with the AAA detection function, it is detected that the authentication server is available. If critical-vlan recovery reinitialize is configured:
- If the port is mac-based access control mode, the port added to Critical VLAN will send the unicast packet to all users in Critical VLAN actively, triggering the user to re-authenticate.
- If the port is port-based access control mode, the port added to Critical VLAN will actively send the multicast packet, triggering the user to re-authenticate.
Table 12-33 Configure Critical VLAN
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current interface. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure Critical VLAN
|
authentication critical-vlan critical-vlan-id
|
Mandatory
By default, do not configure Critical VLAN under the port. The value range is 1-4094.
|
|
Configure port recovery and trigger authentication
|
authentication critical-vlan recovery-action reinitialize
|
Optional
By default, after the authentication server is detected to be available, the port only leaves Critical VLAN.
|

-
The function only supports the RADIUS authentication.
- If the radius and escape function are configured on the device, that is, configure aaa authentication dot1x radius none and critical vlan, when the user authenticates, the authentication server is not available and the user will not enter the Critical VLAN, but escape directly. If only escape function is configured, that is, configure aaa authentication dot1x none and critical vlan, when the user authenticates, the escape function takes effect.
- When only configuring the Guest VLAN function under the port, the user failed to authenticate is in Guest VLAN. When Guest VLAN and Critical VLAN function are configured under the port at the same time, the user fails to authenticate because the authentication server is not available and enters Critical VLAN. If the user fails because of other reason, it enters Guest VLAN.
- For AAA detection function, refer to the configuration of Section AAA.
Configure User Authentication Transfer Function
The user authentication transferring function applies to the scenario where the same user (distinguish based on terminal MAC address) transfers from one authentication port of the same device to another. When the user authentication transferring function is disabled, the user is not allowed to initiate authentication on another authentication port of the device after being authenticated on one port of the device; when the user authentication transferring function is enabled, and after the user is authenticated on one port, the device first deletes the authentication information on the original port after detecting that the user transfers to another authentication port, and then, allows the user to initiate authentication on the new authentication port
Whether or not user authentication transferring function is enabled, the device will record the log when detecting that the user transfers between the authentication ports.
Table 12-34 Configure the user authentication transferring function
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current port. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure the user authentication transferring function
|
authentication station-move { enable | disable }
|
Mandatory
By default, the user authentication transferring function is disabled.
|
Configure Timer Parameters
The timer parameters in the port contain: re-authentication timer, quiet timer, server timeout timer, client timeout timer, MAC address authentication user offline check timer.
Re-authentication timer (re-authperiod): After configuring the re-authentication function in the port, the authentication device regularly initiates the re-authentication request to the client, applicable to the 802.1X authentication.
Quiet timer (quiet-period): When the client reaches the maximum authentication failure times, the authentication device can answer the client authentication request again after the quiet time times out, applicable to the 802.1X authentication and MAC address authentication.
Server timeout timer (server-timeout): If the authentication device does not receive the response packet of the server within the specified time, it is regarded to be disconnected with the server, applicable to the 802.1X authentication and MAC address authentication.
Client timeout timer (supp-timeout): If the authentication device does not receive the response packet of the 802.1X client within the specified time, it is regarded to be disconnected with the user, applicable to the 802.1X authentication.
MAC address authentication user offline check timer (offline-detect): After enabling the MAC address authentication, the port periodically detects whether the user is online, applicable to the MAC address authentication.
Table 12-35 Configure the timer parameters
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current port. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Configure the timer parameters
|
dot1x timeout { re-authperiod re-authperiod-value | quiet-period quiet-period-value | server-timeout server-timeout-value | supp-timeout supp-timeout-value | offline-detect offline-detect-value }
|
Mandatory
By default, the re-authentication time in the port is 3600s; the value range is 5-65535;
The quiet time is 60s; the value range is 1-65535;
The timeout of the server is 30s; the value range is 5-3600;
The timeout of the client is 30s; the value range is 5-3600;
The offline check time of the client is 300s; the value range is 5-3600;
|
Configure MAB Function
When the terminal passes MAC address authentication and needs to pass client authentication to use higher access rights, this function can be enabled.
Table 12-36 Enable the MAB function
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current port. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Enable the 802.1X authentication
|
dot1x port-control { enable | disable }
|
Mandatory
By default, the 802.1X authentication function is disabled in the port.
|
|
Enable the MAC address authentication function
|
dot1x mac-authentication { enable | disable }
|
Mandatory
By default, the MAC address authentication function is disabled on the port.
|
|
Enable the MAB function
|
dot1x after-mac-auth { enable | disable }
|
Mandatory
By default, the MAB function is disabled on the port.
|
Restore Port Default Configuration
Restore the default configuration of the 802.1X authentication and MAC address authentication in the port.
Table 12–37 Restore the default configuration of the port
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current port. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Restore the default configuration of the port
|
dot1x default
|
Mandatory
In the port, disable the 802.1X authentication and MAC address authentication function; the related configuration parameters are restored to the default values and the default configuration parameters do not take effect.
|

-
The command show dot1x is used to view the detailed authentication default configuration parameters.
Configure Port Forced Authentication Domain Function
You can enable this function when you need to forcibly assign the authenticated users on the port to a specified domain for authentication.
After the configuration on the port, the priority of the user's domain is: domain carried by the client user > domain configured under the port > default domain of the system.
Table 12–38 Enable forced authentication domain function
|
Step
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
Enter global configuration mode
|
configure terminal
|
-
|
|
Enter the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode
|
interface interface-name
|
Either
After entering the L2 Ethernet interface configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the current port. After entering the aggregation group configuration mode, the subsequent configuration just takes effect on the aggregation group.
|
|
Enter the aggregation group configuration mode
|
interface link-aggregation link-aggregation-id
|
|
Enable 802.1X forced authentication domain function
|
dot1x authentication domain domain-name
|
Mandatory
By default, do not configure the forced authentication domain in the port.
|
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar![Module quang Inphi]() Module quang Inphi
Module quang Inphi![Module Quang Intel]() Module Quang Intel
Module Quang Intel![Module quang Finisar]() Module quang Finisar
Module quang Finisar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng







.png)