At present, the VST (virtual switching technologies, which combines several horizontal physical devices into a virtual device) technology has gradually become a necessary networking technology for LAN because of its high reliability and easy management. The VST technology realizes the unified management of multiple devices at the same level, but there is still the problem of decentralized management of devices in multi-level network. Especially in the typical two-layer LAN, the access layer uses a large number of access devices, which are large in number and strong in dispersion, and need to be maintained and managed one by one. The management is very cumbersome. In addition, assigning an IP address to these devices will consume a lot of IP address resources, which is undoubtedly a waste under the current shortage of IP address resources.
To solve the above problems, the MVST (mix virtual switching technology) technology is proposed. As shown in the figure below, the core layer of LAN adopts the VST technology to virtualize multiple devices into one logical device, while the MVST (mix virtual switching technology) technology is used vertically, which makes all devices in the LAN virtual as one logical device, forming a unified management domain (MVST domain). The management domain provides a management IP address to the outside, and provides the management and access ability for each device in the LAN. It really realizes "one network, one machine", one network, one IP, and one device can easily manage the whole LAN, greatly simplifying the management.
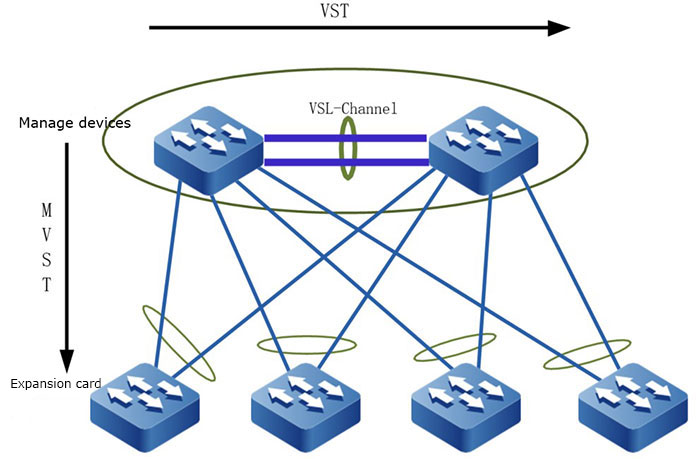
Figure 3-1 MVST physical network view
According to the location and function of the device in the LAN, MVST defines three device roles:
- Master device (MVST master): Responsible for configuring, managing and monitoring all devices in the LAN.
- Extended card (MVST Slave slot): The extended card in the LAN, accepting the unified configuration and management of the master device.
- Candidate card (MVST Candidate): It is not added to the MVST domain, but has the conditions of becoming the extended card.
The master device in the MVST domain discovers the extended card via the MVST detection protocol, collects the information of each extended card in the MVST domain via the MVST topology collection protocol, and draws the LAN topology view. The master device adds the access device to the MVST domain according to the topology view.
After the extended card is added to the MVST domain, the user can log into the control interface of the master device via the IP address of the master device, realizing the unified management for the whole LAN. Besides the general configuration and management, the MVST technology provides the following functions:
- Template configuration
In the application scenario, if some configuration belongs to the public basic configuration and all extended cards in the MVST domain need to apply the configuration, you can edit the configuration to the configuration template and the master device delivers the configuration template to the extended card, which completes the public basic configuration.
- Auto configuration
The master device backs up the startup configuration file of the extended card to the local storage media. When the extended card fails and needs to be replaced with one new extended card, the new extended card does not need any configuration, but directly accesses the LAN via one interface and the master device automatically delivers the backup configuration file to the extended card. In this way, the extended card completes the configuration and the network recovers fast.
- One-key configuration
The master device can enable the Dot1x, storm control, DHCP Snooping, and Arp-check functions of all extended cards in the MVST domain by one key.
- Auto upgrade
The master device prepares the IOS of the extended card in advance. When the extended card is added to the MVST domain, the master device automatically detects whether the running version of the extended card is consistent with the auto upgrade version. If not consistent, the background executes the auto upgrade. On the visible interface of the user, print the log information. When the extended card upgrades, the user still can manage the master device or extended card.
- Password dynamic management
In the MVST domain, the login passwords of all extended cards are generated by the master device dynamically. After the extended card is added to the MVST domain successfully, the master device generates the dynamic password and delivers the password to the extended card. If the extended card needs to log in via console directly during running, the login password can only be got by the master device, strengthening the LAN security.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng




.png)
























