Network Requirements
- Device1, Device2, and Device3 configure the IPv6 static route, making PC1 and PC2 communicate with each other.
Network Topology
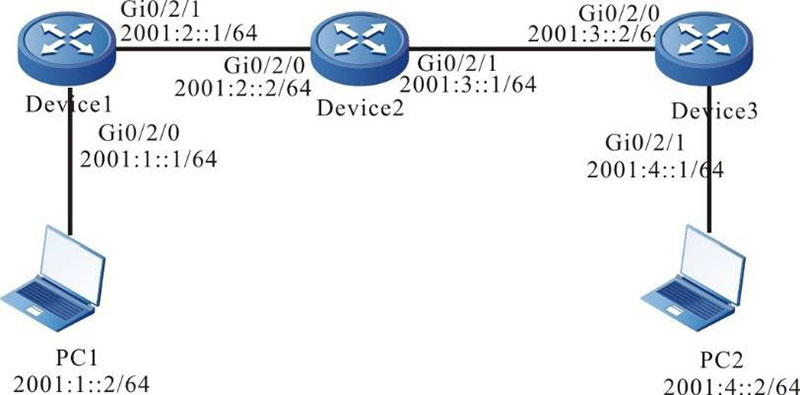
Figure 4-1 Networking for configuring the basic functions of the IPv6 static route
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Configure the IPv6 address of the interface (omitted).
Step 2: Configure the IPv6 static route.
#Configure the IPv6 route on Device1.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config)#ipv6 route 2001:4::/64 2001:2::2
|
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config)#ipv6 route 2001:1::/64 2001:2::1
Device2(config)#ipv6 route 2001:4::/64 2001:3::2
|
#On Device3, configure the IPv6 route.
|
Device3#configure terminal
Device3(config)#ipv6 route 2001:1::/64 2001:3::1
|
#Query the IPv6 route table of Device1.
Device1#show ipv6 route
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
U - Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
S 2001:4::/64 [1/10]
via 2001:2::2, 00:03:14, gigabitethernet0/2/1
L ::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 2w0d:01:09:06, lo0
C 2001:1::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 00:25:55, gigabitethernet0/2/0
L 2001:1::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 00:25:53, lo0
C 2001:2::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 04:01:46, gigabitethernet0/2/1
L 2001:2::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 04:01:45, lo0
#Query the IPv6 route table of Device2.
Device2#show ipv6 route
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
U - Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
L ::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 5w2d:23:52:04, lo0
S 2001:1::/64 [1/10]
via 2001:2::1, 00:02:56, gigabitethernet0/2/0
C 2001:2::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 04:00:52, gigabitethernet0/2/0
L 2001:2::2/128 [0/0]
via ::, 04:00:50, lo0 C 2001:3::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 04:00:20, gigabitethernet0/2/1
L 2001:3::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 04:00:19, lo0
S 2001:4::/64 [1/10]
via 2001:3::2, 00:02:36, gigabitethernet0/2/1
#Query the IPv6 route table of Device3.
Device3#show ipv6 route
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
U - Per-user Static route
O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
S 2001:1::/64 [1/10]
via 2001:3::1, 00:00:08, gigabitethernet0/2/0
L ::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 1w2d:20:54:36, lo0
C 2001:3::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 03:58:28, gigabitethernet0/2/0
L 2001:3::2/128 [0/0]
via ::, 03:58:26, lo0
C 2001:4::/64 [0/0]
via ::, 00:11:13, gigabitethernet0/2/1
L 2001:4::1/128 [0/0]
via ::, 00:11:12, lo0
Step 3: Check the result. Use the ping command to check the connectivity of PC1 and PC2.
#On PC1, use the ping command to check the connectivity.
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>ping 2001:4::2
Pinging 2001:4::2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 2001:4::2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 2001:4::2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 2001:4::2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 2001:4::2: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 2001:4::2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
PC1 and PC2 can communicate with each other.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar![Module quang Inphi]() Module quang Inphi
Module quang Inphi![Module Quang Intel]() Module Quang Intel
Module Quang Intel![Module quang Finisar]() Module quang Finisar
Module quang Finisar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng







.png)
























