Network Requirements
- The IRMP protocol operates among Device1, Device2, Device3, and Device4 for routing interaction,
- Device1 learns the routing 200.0.0.0/24 from Device2 and Device3 at the same time. Modify the bandwidth of interface gigabitethernet1 on Device1 to enable Device1 to preferentially choose the routing 200.0.0.0/24 learned from Device2.
- Device1 is required to transfer data to the network segment200.0.0.0/24 simultaneously on lines Device1→Device2→Device4 and Device1→Device3→Device4.
Network Topology
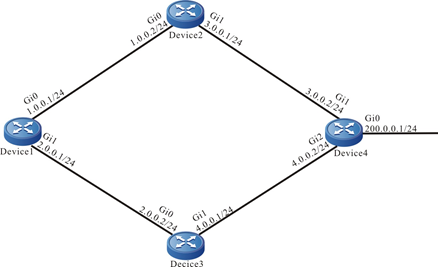
Figure 11–6 Networking of the IRMP unequal-cost load balancing
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Configure the IP address of the interfaces. (Omitted)
Step 2: Configure the IRMP.
#Configure Device1.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config)#router irmp 100
Device1(config-irmp)#network 1.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device1(config-irmp)#network 2.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device1(config-irmp)#exit
|
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config)#router irmp 100
Device2(config-irmp)#network 1.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device2(config-irmp)#network 3.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device2(config-irmp)#exit
|
#Configure Device3.
|
Device3#configure terminal
Device3(config)#router irmp 100
Device3(config-irmp)#network 2.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device3(config-irmp)#network 4.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device3(config-irmp)#exit
|
#Configure Device4.
|
Device4#configure terminal
Device4(config)#router irmp 100
Device4(config-irmp)#network 3.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device4(config-irmp)#network 4.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device4(config-irmp)#network 200.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device4(config-irmp)#exit
|
#View the IRMP neighbor inofrmation of Device1.
Device1#show ip irmp neighbor
IP-IRMP neighbors for process 100 Total neighbor 2
Address Interface Hold(s) Uptime SeqNum Srtt(ms) Rto(s)
1.0.0.2 gigabitethernet0 11 00:10:37 10 0 2
2.0.0.2 gigabitethernet1 12 00:10:15 9 0 2
#View the IRMP neighbor information of Device4.
Device4#show ip irmp neighbor
IP-IRMP neighbors for process 100 Total neighbor 2
Address Interface Hold(s) Uptime SeqNum Srtt(ms) Rto(s)
3.0.0.1 gigabitethernet1 14 00:11:37 13 0 2
4.0.0.1 gigabitethernet2 12 00:10:45 12 0 2
Device1 successfully establishes the IRMP neighbor with Device2 and Device3, respectively. Device4 successfully establishes the IRMP neighbor with Device2 and Device3, respectively.
#View the topology table and routing table of Device1.
Device1#show ip irmp topology
IP-IRMP Topology Table for process 100
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, H - Holddown, D - Hidden
> - FIB route, * - FIB successor
P >1.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 2816
*via Connected (2816/0), gigabitethernet0
P >2.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 2816
*via Connected (2816/0), gigabitethernet1
P >3.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 3072
*via 1.0.0.2 (3072/2816), gigabitethernet0
P >4.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 3072
*via 2.0.0.2 (3072/512), gigabitethernet1
P >200.0.0.0/24, 2 successors, FD is 3328
*via 2.0.0.2 (3328/3072), gigabitethernet1
*via 1.0.0.2 (3328/3072), gigabitethernet0
Device1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 1.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 13:16:35, gigabitethernet0
C 2.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 13:19:24, gigabitethernet1
E 3.0.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 1.0.0.2, 00:03:22, gigabitethernet0
E 4.0.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 2.0.0.2, 00:22:01, gigabitethernet1
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 22:27:25, lo0
E 200.0.0.0/24 [90/3328] via 2.0.0.2, 00:21:22, gigabitethernet1
[90/3328] via 1.0.0.2, 00:03:22, gigabitethernet0
There are two load balancing routing to the network segment 200.0.0.0/24 in Device1 routing table. The forwarding paths to the network segment are Device1→Device2→Device4 and Device1→Device3→Device4.
Step 3: Change the interface delay.
#Change the bandwidth of the interface connected to Device1 and Device3 to 100000 kbps.
|
Device1(config)#interface gigabitethernet1
Device1(config-if-gigabitethernet1)#bandwidth 100000
Device1(config-if-gigabitethernet1)#exit
|
#View the topology table and routing table of Device1.
Device1#show ip irmp topology
IP-IRMP Topology Table for process 100
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, H - Holddown, D - Hidden
> - FIB route, * - FIB successor
P >1.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 2816
*via Connected (2816/0), gigabitethernet0
P >2.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 25856
*via Connected (25856/0), gigabitethernet1
P >3.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 3072
*via 1.0.0.2 (3072/2816), gigabitethernet0
P >4.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 26112
*via 2.0.0.2 (26112/2816), gigabitethernet1
P >200.0.0.0/24, 2 successors, FD is 3328
*via 1.0.0.2 (3328/3072), gigabitethernet0
via 2.0.0.2 (26368/3072), gigabitethernet1
Device1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 1.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 28:44:11, gigabitethernet0
C 2.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:14:05, gigabitethernet1
E 3.0.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 1.0.0.2, 00:10:11, gigabitethernet0
E 4.0.0.0/24 [90/28416] via 2.0.0.2, 00:07:57, gigabitethernet1
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 220:26:51, lo0
E 200.0.0.0/24 [90/3328] via 1.0.0.2, 00:10:11, gigabitethernet0
After the metric offset is configured, Device1 preferentially chooses the routing 200.0.0.0/24 advertised by Device2.
Step 4: Configure the IRMP unequal-cost load balancing.
#Configure Device1 and configure the load balancing conversion factor as 100.
|
Device1(config)#router irmp 100
Device1(config-irmp)#variance 100
Device1(config-irmp)#exit
|
For details about the load balancing conversion factor, refer to the load balancing chapter in the IRMP function configuration.
Step 5: Check the result.
#View the topology table and routing table of Device1.
Device1#show ip irmp topology
IP-IRMP Topology Table for process 100
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, H - Holddown, D Hidden
> - FIB route, * FIB successor
P >1.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 2816
*via Connected (2816/0), gigabitethernet0
P >2.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 28160
*via Connected (28160/0), gigabitethernet1
P >3.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 3072
*via 1.0.0.2 (3072/2816), gigabitethernet0
P >4.0.0.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 28416
*via 2.0.0.2 (28416/2816), gigabitethernet1
P >200.0.0.0/24, 2 successors, FD is 3328
*via 1.0.0.2 (3328/3072), gigabitethernet0
*via 2.0.0.2 (26368/3072), gigabitethernet1
Device1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M - Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B - BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 1.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 28:47:15, gigabitethernet0
C 2.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:17:08, gigabitethernet1
E 3.0.0.0/24 [90/3072] via 1.0.0.2, 00:13:15, gigabitethernet0
E 4.0.0.0/24 [90/28416] via 2.0.0.2, 00:11:00, gigabitethernet1
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 220:29:54, lo0
E 200.0.0.0/24 [90/3328] via 1.0.0.2, 00:13:15, gigabitethernet0
[90/26368] via 2.0.0.2, 00:00:12, gigabitethernet1
Routing 200.0.0.0/24 on Device1 forms the unequal-cost load balancing. Data will be transmitted for load balancing on these two paths based on the inverse ratio of the metric value.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar![Module quang Inphi]() Module quang Inphi
Module quang Inphi![Module Quang Intel]() Module Quang Intel
Module Quang Intel![Module quang Finisar]() Module quang Finisar
Module quang Finisar Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng







.png)
























