Network Requirements
- Run OSPF between Device1 and Device2, and run RIPv2 between Device2 and Device3.
- Device2 redistributes RIP routes to OSPF, and it uses a route policy to control the device to only redistribute route 100.0.0.0/24.
Network Topology
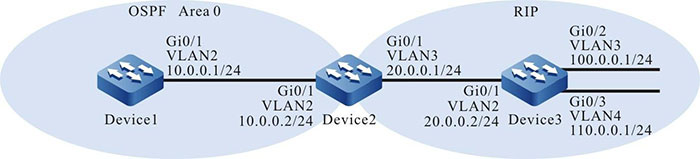
Figure 7-3 Networking for Configuring OSPF to Redistribute Routes
Configuration Steps
Step 1: Create VLANs, and add ports to the required VLANs. (Omitted)
Step 2: Configure IP addresses for the ports. (Omitted)
Step 3: Configure OSPF between Device and Device2. Configure RIPv2 between Device2 and Device3.
#Configure OSPF for Device1.
|
Device1#configure terminal
Device1(config)#router ospf 100
Device1(config-ospf)#router-id 1.1.1.1
Device1(config-ospf)#network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device1(config-ospf)#exit
|
#Configure OSPF and RIPv2 for Device2.
|
Device2#configure terminal
Device2(config)#router ospf 100
Device2(config-ospf)#router-id 2.2.2.2
Device2(config-ospf)#network 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Device2(config-ospf)#exit
Device2(config)#router rip
Device2(config-rip)#version 2
Device2(config-rip)#network 20.0.0.0
Device2(config-rip)#exit
|
#Configure RIPv2 for Device3.
|
Device3#configure terminal
Device3(config)#router rip
Device3(config-rip)#version 2
Device3(config-rip)#network 20.0.0.0
Device3(config-rip)#network 100.0.0.0
Device3(config-rip)#network 110.0.0.0
Device3(config-rip)#exit
|
#Query the OSPF neighbor information of Device2.
Device1#show ip ospf neighbor OSPF process 100:
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
2.2.2.2 1 Full/DR 00:00:32 10.0.0.2 vlan2
#Query the OSPF neighbor information of Device2.
Device2#show ip ospf neighbor OSPF process 100:
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
1.1.1.1 1 Full/Backup 00:00:32 10.0.0.1 vlan2
#Query the routing table of Device2.
Device2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:21:17, vlan2
C 20.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:21:33, vlan3
R 100.0.0.0/24 [120/1] via 20.0.0.2, 00:10:58, vlan3
R 110.0.0.0/24 [120/1] via 20.0.0.2, 00:10:58, vlan3
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 30:20:17, lo0
RIP routes have been learnt by Device2.
Step 4: Configure the routing policy.
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2(config)#ip access-list standard 1
Device2(config-std-nacl)#permit 100.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Device2(config-std-nacl)#exit
Device2(config)#route-map RIPtoOSPF
Device2(config-route-map)#match ip address 1
Device2(config-route-map)#exit
|
The route-map is configured to invoke an ACL to match only 100.0.0.0/24 while filtering out other network segment, such as 20.0.0.0/24 and 110.0.0.0/24.
Step 5: Configure OSPF to redistribute RIP routes and associate a routing policy.
#Configure Device2.
|
Device2(config)#router ospf 100
Device2(config-ospf)#redistribute rip route-map RIPtoOSPF
Device2(config-ospf)#exit
|
In redistributing RIP routes, the route-map matching rule is invoked for filtration.
Step 6: Check the result.
#Query the routing table of Device1.
Device1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF, OE-OSPF External, M Management
D - Redirect, E - IRMP, EX - IRMP external, o - SNSP, B BGP, i-ISIS
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, 00:47:27, vlan2
OE 100.0.0.0/24 [150/20] via 10.0.0.2, 00:21:39, vlan2
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, 21:40:06, lo0
The routing table of Device1 has learnt only the OSPF external route 100.0.0.0/24 while routes 20.0.0.0/24 and 110.0.0.0/24 have been filtered out.
#Query the OSPF process information and database of Device2.
Device2#show ip ospf 100
Routing Process "ospf 100" with ID 2.2.2.2
Process bound to VRF default
Process uptime is 1 hour 4 minutes
IETF NSF restarter support disabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Conforms to RFC2328, and RFC1583Compatibility flag is disabled
Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes
Supports opaque LSA
Supports Graceful Restart
This router is an ASBR (injecting external routing information)
Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs
Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs
Refresh timer 10 secs
Number of external LSA 2. Checksum Sum 0x0161F5
Number of opaque AS LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000
Number of non-default external LSA is 2
External LSA database is unlimited.
Not Support Demand Circuit lsa number is 0, autonomy system support flood DoNotAge Lsa
Number of areas attached to this router: 1
Area 0 (BACKBONE) Number of interfaces in this area is 1(1)
Number of fully adjacent neighbors in this area is 1
Number of fully adjacent sham-link neighbors in this area is 0
Area has no authentication
SPF algorithm last executed 00:37:52.833 ago
SPF algorithm executed 3 times
Number of LSA 3. Checksum Sum 0x00e746
Not Support Demand Circuit lsa number is 0,
Indication lsa (by other routers) number is: 0,
Area support flood DoNotAge Lsa
Device2#show ip ospf 100 database
OSPF Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 100)
Router Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Link count
1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 191 0x80000004 0x70a0 1
2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 537 0x80000005 0x36ce 1
Net Link States (Area 0)
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum
10.0.0.2 2.2.2.2 818 0x80000003 0x3fd8
AS External Link States
Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Route
100.0.0.0 2.2.2.2 718 0x80000002 0x72be E2 100.0.0.0/24 [0x0]
According to the information about OSPF process 100, Device2 has changed its role to become an ASBR, and only one external LSA has been generated in the database.

-
In an actual application, if there are two or more AS boundary routers, it is recommended that you do not redistribute routes between different routing protocols. If you really need to redistribute routes between different routing protocols, configure a routing policy to prevent routing loops.
 Switch
Switch Wifi - Access Point
Wifi - Access Point Firewall
Firewall Router
Router Module Quang
Module Quang![Module Quang Cisco]() Module Quang Cisco
Module Quang Cisco![Module quang HPE]() Module quang HPE
Module quang HPE![Module quang Maipu]() Module quang Maipu
Module quang Maipu![Module quang Brocade]() Module quang Brocade
Module quang Brocade![Module quang Fortinet]() Module quang Fortinet
Module quang Fortinet![Module quang Aruba]() Module quang Aruba
Module quang Aruba![Module quang OEM]() Module quang OEM
Module quang OEM![Module quang Juniper]() Module quang Juniper
Module quang Juniper![Module quang Dell]() Module quang Dell
Module quang Dell![Module quang Palo Alto]() Module quang Palo Alto
Module quang Palo Alto![Module quang Huawei]() Module quang Huawei
Module quang Huawei![Module quang Arista]() Module quang Arista
Module quang Arista![Module quang F5]() Module quang F5
Module quang F5![Module quang H3C]() Module quang H3C
Module quang H3C![Module Quang Allied Telesis]() Module Quang Allied Telesis
Module Quang Allied Telesis![Module quang SonicWall]() Module quang SonicWall
Module quang SonicWall![Module quang Mikrotik]() Module quang Mikrotik
Module quang Mikrotik![Module quang Handar]() Module quang Handar
Module quang Handar![Module quang Inphi]() Module quang Inphi
Module quang Inphi![Module Quang Intel]() Module Quang Intel
Module Quang Intel![Module quang Finisar]() Module quang Finisar
Module quang Finisar![Module quang Ascent]() module-quang-ascent
module-quang-ascent Máy chủ (Server)
Máy chủ (Server) Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS)
Thiết bị lưu trữ (SAN, NAS) Load Balancing
Load Balancing Video Conferencing
Video Conferencing Phụ kiện máy chủ
Phụ kiện máy chủ Thiết Bị IoT
Thiết Bị IoT Phụ Kiện Mạng
Phụ Kiện Mạng








.png)
























